Mesenchymal Stem Cells -extracellular vesicles in neuronal cell survival
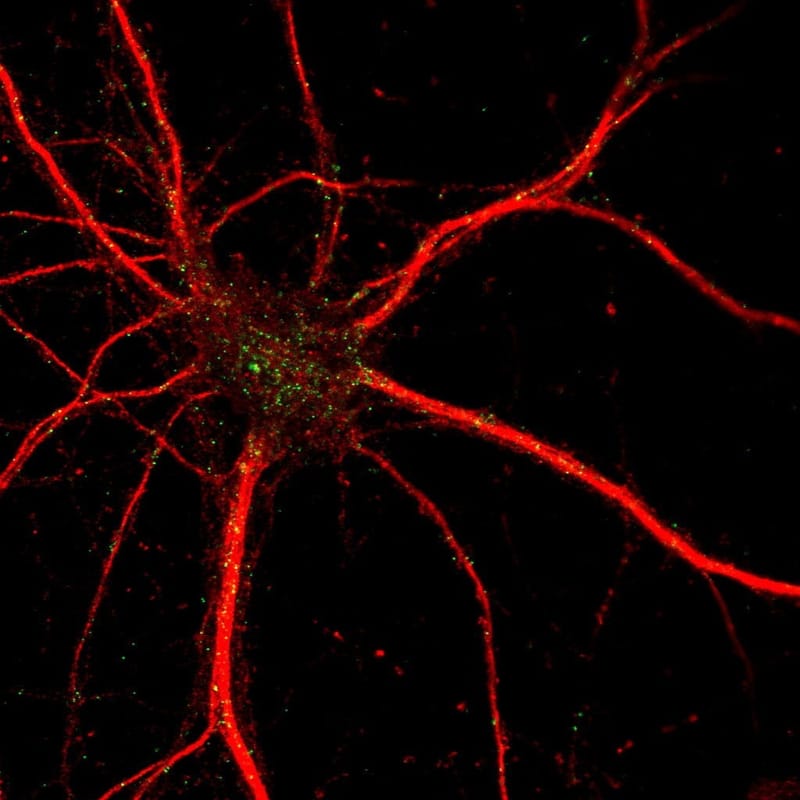
Tracking neuroprotection of selected mesenchymal stem cell-extracellular vesicle cargo
Mesenchymal stem cells are found throughout the human body. Mesenchymal stem cells not only have the potential to differentiate into adipocytes, osteoblasts, and chondrocytes, both in vivo and in vitro, but they also possess immunomodulatory and regenerative properties. Current thinking attributes the regenerative properties of the mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) secretome to bioactive molecules found in the cargo of their extracellular vesicles (EVs). However, MSC-EV-mediated cell regeneration and, in particular, the underlying mechanism of MSC-EV neuroprotection are poorly understood.
The main objective of this project was to identify and track the MSC-EVs neuroprotective cargo. To do so, the proteomics and transcriptomics content of MSC-derived EVs was compared to that of EVs secreted by primary fibroblasts, which are a mesenchymal cell-type but without the regeneration property of MSC. (Tonoli et. al 2022).
We are testing potential MSC-EV-specific bioactive molecules (proteins, miRNA, and cytokines) by employing in vitro mouse brain neurons, human iPSC-derived neurons Alzheimer's disease (AD) model, and an in vivo C. elegans AD model.
In the future, by employing an organ-on-chip 3D-blood brain barrier (BBB) model of the brain, we will test potential MSC-EV-specific cargo for delivery across the BBB to neurons, via a synthetic lipid nanoparticle delivery system.